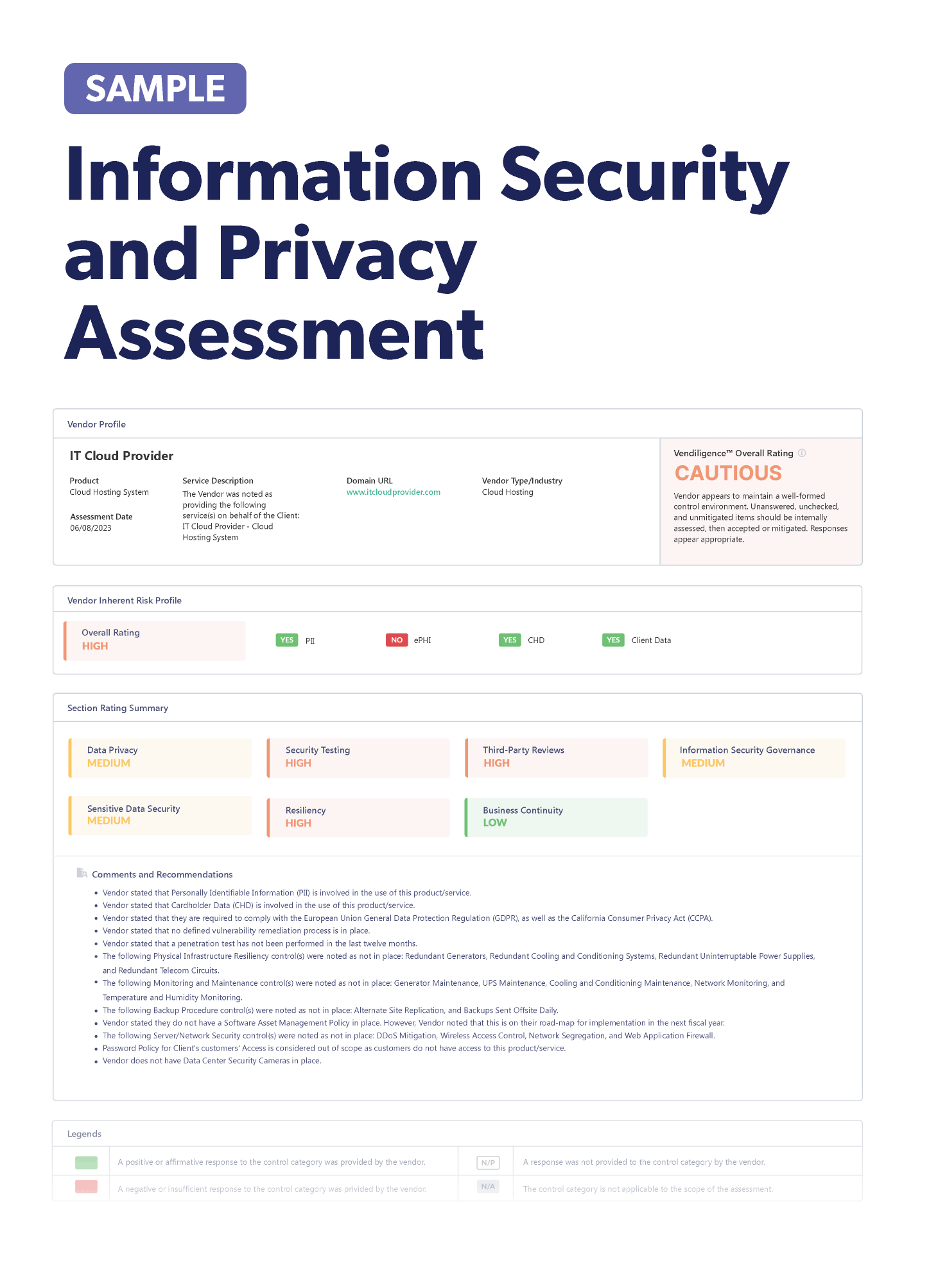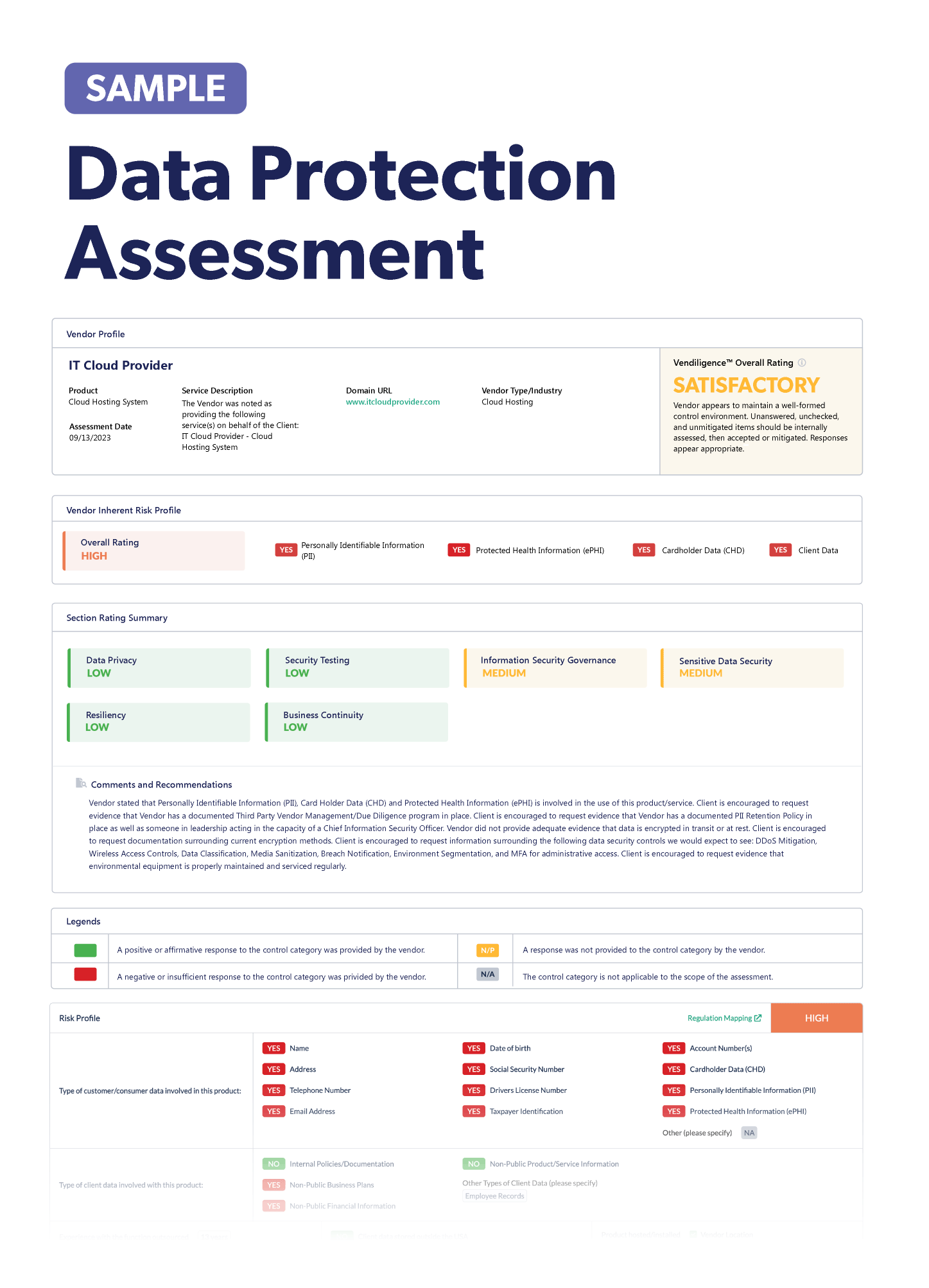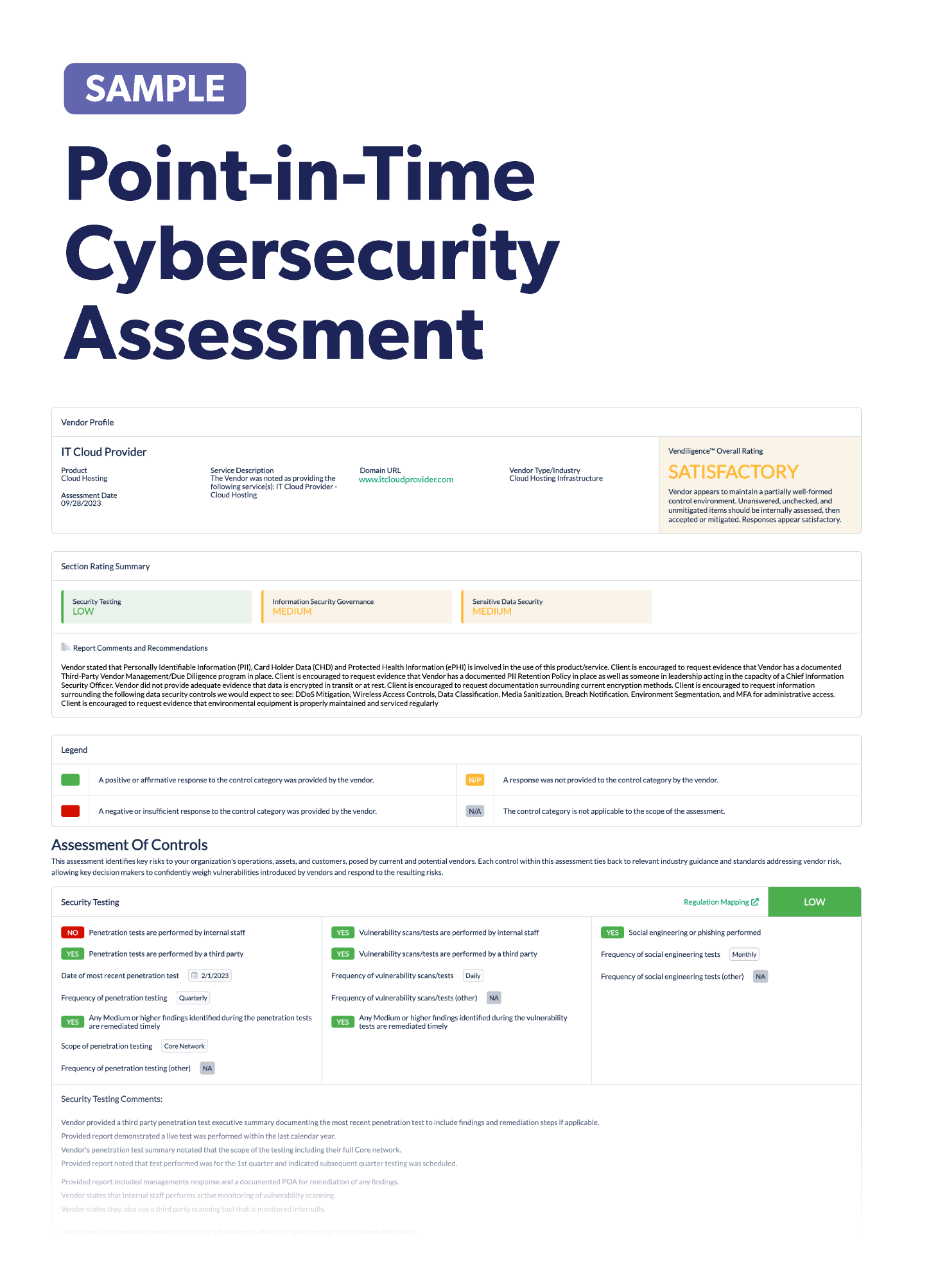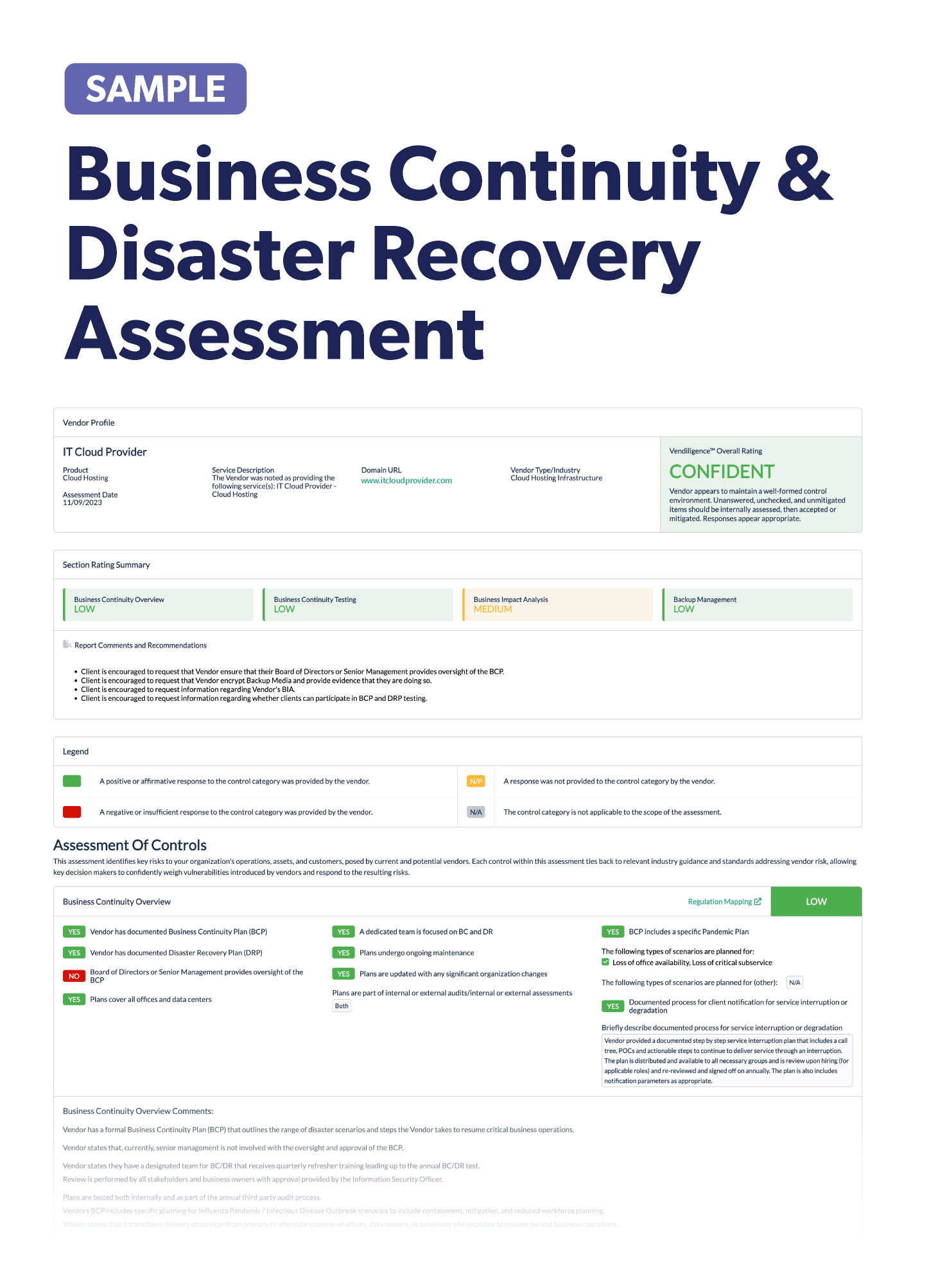
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor management news happening this month. Discover information to help improve or freshen up your third-party risk management program. Below are some articles you should check out.
Recently Added Articles as of April 28
The invasion of Ukraine continues to threaten critical infrastructure and the FBI is warning about the Blackcat ransomware-as-a-service. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security's bug bounty revealed over 100 vulnerabilities and the CFPB is turning a more critical eye towards non-banks. Third-party risk management needs to be improved in the healthcare sector and a healthcare vendor is being sued for a concealed ransomware incident. Read on for all the details!
Hundreds of vulnerabilities found during DHS program: The first bug bounty from the Department of Homeland Security appears to be a success, with a total of 122 vulnerabilities discovered (22% critical). Phase one of the Hack DHS bounty began last December and participants were rewarded between $500-$5,000 for each discovered bug. DHS stated that they look forward to strengthening their relationship with the researcher community as they help find and remediate critical vulnerabilities. With all the headlines of criminal hackers causing destruction, it’s reassuring to know that there are good hackers in the world, too!
Threat actors fix bug to re-distribute Emotet malware: Sometimes software bugs work in favor of the intended victim, preventing a malicious action from taking place. Such was the case with a recent Emotet malware phishing campaign which included Windows LNK files disguised as Word documents. Unfortunately, the Emotet campaign is back spreading around malicious attachments after the threat actors fixed the bug, allowing the malware to work as intended. Some of the file names Emotet is using are form.zip, Payment Status.zip, BANK TRANSFER COPY.zip and ACH payment info.zip. If you receive an email with a similar password-protected attachment, experts urge users to avoid opening it and instead contact their network or security admininstrators for further instructions. Ensure that individuals throughout your organization, and your third parties, practice good cybersecurity hygiene, because threat actors are always working!
Vulnerability found in crypto wallet Ever Surf: The Everscale blockchain wallet named Ever Surf contains an exploitable vulnerability that would allow attackers to gain full control of a victim’s cryptocurrency. Malicious browser extensions or phishing links can be used as attack vectors to obtain the wallet’s encrypted keys. The vulnerable web version has been replaced by a new desktop act, but security experts warn that users may be exposed to other vulnerabilities in decentralized applications or basic threats like fraud and phishing scams. With cryptocurrency growing in popularity, it’s essential to stay informed of the vulnerabilities and threats that could impact users.
CFPB to begin using dormant authority on non-banks: The CFPB is making an effort to hold non-banks to the same standards as supervised banks with a goal to stop harm from potentially risky financial companies. The agency announced that it’s invoking a legal provision to examine non-banks that put consumers at risk. The CFPB can find cause to act based on sources from judicial opinions, administrative decisions, whistleblower complaints, state or federal partners and news reports. Non-banks often brand themselves as “fintechs,” and the agency aims to “level the playing field” between the two types of financial providers. Another priority for the CFPB is transparency in the risk-determination process, outlined in a procedural rule. With regulators increasing their focus on non-banks, it should be interesting to see whether this scrutiny trickles down to the state level.
Hard drive disposal can lead to health record breaches: Data breaches are often thought of in terms of vulnerabilities within existing systems. However, the HIPAA Security Rule also highlights the importance of data destruction when it comes to end-of-life electronics. In other words, healthcare providers must have policies and procedures in place to properly dispose of computers and electronics and failure to do so can lead to data theft. Destroying data refers to sanitizing the information on the hard drive or storage device before the item is recycled or restored to factory settings. An incident in September of 2021 was linked to a possible violation of improper hard drive disposal. It should be noted that healthcare data breaches due to negligence can lead to fines, so it’s essential to comply with HIPAA regulations.
FBI releases Flash report on BlackCat Ransomware: According to a recent FBI Flash report, at least 60 organizations around the world have been impacted by the BlackCat ransomware-as-a-service. The group works by stealing data prior to executing the ransomware, often using compromised user credentials to gain access. The FBI advises to quickly report any ransomware incidents and doesn’t encourage victims to pay the ransom as it doesn’t guarantee the recovery of stolen files. The advisory also covers a list of recommended mitigations, such as reviewing domain controllers, regularly backing up data and implementing network segmentation, which are all practices that should be implemented in any standard cybersecurity program.
Three vendor risk management tips for startups: The startup culture is inherently risky and even more so when you consider the third-party vendors that are involved. Startups need agility when beginning their operations and a wrong vendor can quickly and easily jeopardize the company’s sustainability. For startups to build a successful vendor risk management strategy, they should focus on three simple concepts. First, it’s important to continue monitoring vendors. Ongoing monitoring is just as important as the initial due diligence as you can get a better sense of the long-term relationship. Second, business leaders should prepare for their staffing needs and figure out how to best gain efficiency while still performing proper due diligence. And, finally, it’s important to assess risk well. Make sure to implement good inherent risk processes to determine due diligence requirements. This process will help determine appropriate contract clauses and monitoring requirements or may even lead to ending the partnership.
CISA warns of state-sponsored Russian cyber threats: A multi-national advisory has been released, warning about increased malicious cyber activity related to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The advisory notes that some cybercrime groups have pledged support for Russia and have threatened to retaliate against supporters of Ukraine. Individuals in the critical infrastructure network are being urged to be prepared for and mitigate cyber threats by updating software, enforcing multifactor authentication and providing end-user awareness and training for social engineering tactics. The advisory also provides details on identity and access management, protective controls and architecture and how to respond to cyber incidents. It’s evident that the invasion of Ukraine is having a global impact, so it’s critical to stay aware of any risks that can affect your organization.
More needs to be done with managing third-party identities: Research shows that 78% of organizations use multiple identity records for a single third party. The problem is, this leads to inaccurate or outdated information. Third-party workers might be linked to projects that they’re no longer working on and, therefore, don’t need to access them. Using multiple active identifies can increase vulnerabilities to security breaches. Another troubling statistic was that only 53% of organizations are verifying third-party individuals before giving them access to their assets. Many respondents were also failing to deactivate users after they’re no longer qualified to perform duties. Most breaches are the result of compromised credentials, so these poor security practices are leaving many organizations vulnerable. Investing in the right tools and services can help organizations stay safe within high-risk third-party relationships.
Healthcare security leader speaks on TPRM: Assistant Vice President of IT security at Mount Sinai South Nassau, Chris Frenz, recently spoke about the importance of third-party risk management. Referencing the notable incidents involving Okta and Log4j, Frenz stated that his team is starting to incorporate more questions about software bill of materials in their risk assessment process. He notes that this strategy gives them better visibility into whether a vendor is using an affected product. He also highlights the importance of vendors being transparent about software vulnerabilities and speaks to some of the challenges related to patch management. The Russia-Ukraine war has also triggered the need to be extra prepared for potential cyber incidents.
Improvement needed for TPRM in healthcare: It’s well known that the healthcare industry is one of the top targets for cyberattacks, but many organizations still aren’t too confident in their third-party risk management and compliance strategies. Sixty percent (60%) of surveyed healthcare organizations said that their TPRM programs need some improvement. The survey revealed inefficiencies around communications as well as significant security gaps within third-party systems. Email security incidents were to blame for many recent data breaches and only 47% of respondents said that all their sensitive content email was encrypted. Ransomware, DDoS attacks and malware were also concerning for many healthcare leaders. So, the message is clear – third-party risk management needs to be a priority for the healthcare industry, especially as the threat landscape continues to evolve and become more sophisticated.
Concealed ransomware attack leads to vendor lawsuit: North Carolina-based healthcare vendor, Eye Care Leaders (ECL), is in hot water after failing to send a timely notice after a series of ransomware attacks. Three of its customers filed a lawsuit, claiming that ECL concealed a ransomware attack which led to a whole host of problems like lost data, business disruptions and reputational damage. ECL was contracted to provide revenue lifecycle management and electronic medical records maintenance for the three plaintiffs, and this isn’t the company’s first brush with controversy. Just last year, ECL’s sole manager, Greg E. Lindberg, was sentenced to 87 months in prison for charges related to wire fraud and bribery. This case highlights a number of critical third-party risk management lessons. Most notably, the importance of initial and ongoing vendor due diligence as well as business continuity planning.
Industrial control systems targeted by versatile malware: The Feds are warning of a new malware toolkit known as Pipedream, which researchers say essentially acts as a Swiss Army knife on a wide range of industrial control systems like power grids, oil refineries and water utilities. A recent interagency advisory was released, warning about the custom-made tools which can scan, compromise and control affected devices. Programmable logic controllers sold by Schneider Electric and OMRON were identified in the advisory as being vulnerable to the malware. The toolkit is especially worrisome because of its adaptability and expansiveness, with the potential to cause significant life-threatening destruction if used on petrochemical facilities. The advisory contains a list of proactive mitigations for organizations with ICS/SCADA devices, noting that they should be tested before being implemented.
Google apps shut down after harvesting data: Apps for QR scanning and weather were just some of the ones recently removed from Google’s Play Store after it was revealed that they contained malicious code to illegally harvest locations, phone numbers and email addresses. Researchers discovered that the apps contained a software development kit (SDK) which would send user data to a third party. In the past, Google warned app developers that they need to be transparent with users about the data they share and failing to comply can lead to a ban from the app store. However, apps are free to be reinstated if they remove the illegal code. While being temporarily banned from an app store might be an inconvenience, developers should consider the larger consequences of failing to comply with data privacy laws that are continuing to crop up across the globe.
Recently Added Articles as of April 21
Cryptocurrency, blockchain technology and foreign hackers are all in the news this week which have led to a few significant advisories. Read up on how third-party risk management can benefit from blockchain and why crypto firms need to strengthen their cybersecurity. LinkedIn is the most spoofed brand in phishing attacks and North Korean hackers are behind a record-breaking crypto theft. Read on for all the details!
The pros and cons of blockchain in third-party risk management: Compliance professionals often rely on big data, artificial intelligence and machine learning to manage third-party risk, but a new technology may be ready to join the team. Blockchain has amassed quite an impressive following with Bill Gates calling it a “technological tour de force” and Gartner stating that it’ll transform most industries. So how exactly can blockchain be used in third-party risk management? Compliance teams would have access to updated background information on third parties without the need for lengthy and time-consuming questionnaires. Blockchain would allow organizations to track compliance benchmarks in real time and the data can’t be modified so its integrity stays intact. However, blockchain isn’t completely free of risk. There’s still the potential for malicious entities to gain majority control of a blockchain’s nodes in an event called a 51 percent attack. Speed and scalability are also issues that need to be addressed as the technology slows down with more users. It’ll likely be a while before we see widespread adoption of blockchain technology, but the possibilities are worth considering.
Hackers most likely to spoof LinkedIn: Phishing attacks often rely on mimicking trustworthy brands or individuals to fool users and LinkedIn has been named as the most spoofed brand. Over 50% of all global phishing attacks have used fake LinkedIn branding to request fraudulent connections. Experts warn that social media phishing attacks are on the rise because they enable threat actors to perform additional attacks like spear-phishing posting links to malware sites or sending spyware. DHL, Google, Microsoft and FedEx are just a few other commonly spoofed brands. While it’s important to stay aware of hacking trends on a personal level, don’t forget to do the same for your organization’s cybersecurity program.
Blockchain under attack by North Korean hackers: Despite the benefits that many experts see in blockchain technology, don’t assume that they’re safe from hackers. CISA, the FBI and the Treasury recently released a joint statement warning about malicious activity targeting blockchain companies. The infamous North Korean-backed Lazarus Group is behind the string of ongoing cyberattacks which begin with spear-phishing messages sent to employees. The three agencies state that these threat actors will continue to exploit vulnerabilities in cryptocurrency firms and gaming companies which should serve as an important reminder to implement mitigation strategies such as patch management, social engineering education and multifactor authentication.
The exploitation of QR codes: Quick response (QR) codes are more common than ever, so it’s a good idea to be aware of how threat actors are exploiting them in attacks known as “Qshing”. While attackers can’t directly compromise a QR code, they can substitute it with another to distribute malicious software or redirect users to a malicious site. According to an FBI warning issued in January, attackers are often going after credentials and money. There are a few tips to consider when scanning a QR code. First, use a security app as another layer of protection. Assess the code’s credibility and whether it’s requesting information that doesn’t seem relevant to the application. You may also consider bypassing the QR code and downloading applications directly from the URL rather than through the code. You should also confirm the QR code destination by reviewing the URL validity, encryption status and page formatting. Since cybersecurity is often a leading vendor risk, it’s essential to stay informed of various types of cyberattacks that can ultimately affect your organization.
Beware of reverse phishing scams: It seems as though cybercriminals are increasingly using devious methods to carry out their attacks. Rather than gaining unauthorized access to steal funds, criminals are tricking victims to hand over the money themselves. A new FBI advisory is warning about a new phishing scheme where cybercriminals are posing as an organization’s fraud department. Victims are led to believe that they need to go through a process to reverse a fraudulent instant payment transaction and ultimately remove their email address from their digital payment app. The criminals direct the victims to start another transaction to themselves which will supposedly reverse the original fraudulent payment. The FBI warns users to be wary and skeptical of such requests. It’s better to contact your financial institution’s fraud department directly through a verified phone number. As cybercriminals continue to use sophisticated attack methods, it’s more important than ever to take the proper precautions.
Crypto firms advised to strengthen cybersecurity: DeFiance Capital founder, Arthur Cheong, is urging his fellow crypto leaders to stay aware of state-sponsored cybercrime that’s impacting the industry. Crypto firms should be especially careful when hiring remote teams and should revoke unnecessary token approvals. He also suggests having dedicated computers for crypto transactions. North Korea has reportedly increased their crypto-related attacks in recent months and was recently tied to the theft of more than $600 million from a software bridge. As cryptocurrency gains more traction with the public and cybercriminals it should be interesting to see how regulators respond to emerging threats.
Kleptocracy highlighted as concern in FinCEN advisory: Kleptocracy, foreign corruption and Russia were just a few of the top concerns noted by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in their recent advisory targeted towards the financial industry. Kleptocracy refers to the notable characterization of corruption in a government with Russia being a prime example. After the recent invasion of Ukraine, and the subsequent Russian sanctions, FinCEN is warning of some of the red flags that financial institutions should recognize. Transactions that involve services provided to state-owned companies and the use of third parties to hide the identity of foreign public officials are a couple significant red flags. Fictitious email addresses, false invoices and transactions that contained mismatched payments are also to be scrutinized. While the Russia-Ukraine conflict continues to highlight cyber and operational risk within supply chains, it’s important to consider the regulatory risk that can be found in third-party transactions.
North Korea to blame for record-breaking crypto theft: The Ronin blockchain recently suffered a theft of over $600 million cryptocurrency and the FBI has identified North Korea’s Lazarus Group as the guilty party. The FBI issued a press release, in which they stated that U.S. agencies will continue to combat North Korea’s illicit activities like cybercrime and cryptocurrency theft. The address that received the stolen crypto has been sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury, though it’s currently being laundered through a service called Tornado Cash. The theft was made possible by exploiting a vulnerability in the Ronin network, which runs a popular NFT game. While cybercriminals continue to target user credentials and traditional currency, it’s worth noting that cryptocurrency theft seems to be gaining popularity.
The danger of ransomware in healthcare: Critical infrastructure continues to be a popular target for cybercriminals, often resulting in financial loss of an essential service like power. However, some industries can have much more dire consequences. Ransomware on healthcare organizations can ultimately lead to increased mortality, so it’s critical that security professionals take action to protect against cybercriminals. IT and security professionals can begin by identifying and adding all their Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices to their security governance process. They should also identify vulnerabilities and make sure to remediate risks that are linked to those devices. Implementing network segmentation is another important practice and teams should make sure to monitor threats across IoMT devices so they can take specific steps to manage ransomware risks. With the right strategy in place, healthcare organizations can better protect themselves from a wide range of cybersecurity risks.
Managing third-party security risk with enhanced transparency: SolarWinds, Kaseya and Log4J are just a few of the notable third-party security incidents that made waves over the past couple of years. Vulnerabilities are a key component of cybersecurity research, but some experts are emphasizing the importance of visibility and transparency within third-party risks. When third-party software vulnerabilities are discovered, it’s critical that stakeholders have visibility so they can communicate those risks to their partners. Organizations and their security teams should adopt a full operational view of these scenarios, using real-time data to keep everyone informed. Ultimately, it’s better for organizations to operate as if a third-party crisis is imminent, rather than merely a possibility.
How to de-risk the cloud in 3 steps: If you’re preparing to purchase a new SaaS application, this article is for you. Before signing the contract, it’s important to understand some key areas. First, understand that there’s a threat of data loss and that the data recovery might be in a format that’s incompatible for your organization. Remember that you don’t physically possess the software, nor are the applications and data protected just because they’re in the cloud. It’s also important to understand some of the key regulations to ensure compliance. To address these concerns, the first step is to identify and assess the risks so you can track and manage them over time. The second step is to implement a solution for cloud risk management and the final step involves testing your business continuity plan.
Recently Added Articles as of April 14
The invasion of Ukraine has brought more attention to global sanctions, cybersecurity and legal and compliance issues. The healthcare industry in Europe may be unprepared for Russian-related cyber threats and Microsoft helped stop cyberattacks on Ukraine. Learn how to find attack paths in cloud infrastructure and why you need accountability in supply chain security. There’s a lot to uncover this week, so read on for all the details.
Control Risks report on global sanctions: A new report by consulting firm Control Risks dives into the complex sanctions landscape of 2022. The U.S., EU and UK are just some of the regions leading the way in challenging foreign policies by implementing sanctions. The report highlights the challenges found in sanctioning cryptocurrency while also focusing on the need to screen for sanctions within your third-party risk management program. A risk-based approach is ideal when screening for sanctions while human-led due diligence should be performed for high-risk third parties. And, remember that sanctions list are always changing, which requires a healthy practice of ongoing monitoring within your third-party inventory.
Hospital robots contained critical bugs: Hospitals using Aethon Tug robots had a scare recently when it was revealed that five exploitable bugs were discovered that could have enabled criminals to remotely control thousands of their medical machines. If these vulnerabilities hadn’t been patched, there was the potential for accessing user credentials, surveilling facilities and even locking elevators and doors. Security firm Cynerio discovered the bugs and notified the robot manufacturer Aethon who fixed the bugs. Tug robots are highly valuable tools that can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks including transporting medications and delivering supplies. However, this also means that they’re a prime target for cybercriminals who can infiltrate them to be destructive. Staying on top of vulnerabilities requires more than a reactive approach. It’s critical to identify issues before they’re exploited so attackers can’t get the upper hand.
How to find attack paths in the cloud: Many organizations are continuing to adopt cloud infrastructure which offers many advantages as well as risks. Threat actors are highly reactive and adaptable, so it’s wise to assume that organizations are already under attack. To understand which assets are most vulnerable, organizations should map out potential attack paths, which can be done with scanning tools. These tools can determine how access paths affect certain resources and they show the relationships between all cloud-hosted entities. This information is used to identify potential lateral movement and help find ways to block escalation. Cloud infrastructure will likely only continue to grow and evolve, so it’s important to stay aware of the associated risks and understand how to protect your organization.
FDA draft guidance on medical device cybersecurity: Medical devices are increasingly evolving to adopt wireless technology as well as internet and network connected capabilities. Cybersecurity incidents can quickly lead to inoperable hospital networks and medical devices which directly impact the quality of patient care. This has prompted the FDA to release draft guidance that aims to ensure functionality and cybersecurity safety. The guidance will provide industry recommendations on cybersecurity design, labeling and documentation that are to be included in premarket submissions. Cybersecurity threats within the healthcare industry are constantly evolving and becoming more severe, so it’s reassuring to see that regulations are emerging to address these risks.
European healthcare is unprepared for cyber threats: As healthcare providers commonly use electronic health records, data sharing and telehealth, these organizations are being targeted more by hackers. This is becoming even more apparent since the Russian invasion of Ukraine this past February. Experts warn that a system failure within a healthcare environment can be devastating, with two fairly recent incidents in Ireland and Germany supporting this claim. The EU is expected to enhance their cybersecurity strategy later this year to address the ongoing security threats that stem from the rapid digitization of healthcare. Vulnerable interconnected devices and ransomware related to patient data are two of the top concerns. The healthcare industry in Europe is becoming more aware of cyber threats, but experts say that funding continues to be a problem. While many organizations might be familiar with regulations like the GDPR, it’s important to stay aware of the EU’s new strategy regarding cybersecurity.
Cyberattacks target Ukraine and Microsoft responds: Seven domains that were used in ongoing cyberattacks against Ukraine have been seized by Microsoft. The domains were used by Russian state sponsored group Strontium and targeted Ukrainian media organizations and government institutions. Microsoft stated that the domains have been re-directed to a sinkhole, which is used to disrupt the operation of botnets and other malware. This latest incident serves as another reminder of the complexities of modern warfare and its expansion into the cyber world. In a global business environment, it’s critical to stay informed of malicious campaigns that can quickly cross borders.
Atlassian outage not over yet: The recent outage that’s affecting about 400 Atlassian customers may last up to two more weeks. This is an issue that’s being tracked on the company’s status page. The software developer stated that the cause of the outage stems from a routine maintenance script (not a cyberattack), which accidentally disabled a few sites. Though it’s a seemingly small number of users who are still being impacted, the length of the outage is an important reminder of why business continuity and disaster recovery plans are critical to implement and test.
Accountability for supply chain security: Do you want to reduce your third-party risk? If so, you should be clarifying exactly who’s responsible for supply chain risk management – your organization or your suppliers. New research shows that one-third of cybersecurity professionals are taking the responsibility for preventing and detecting supply chain attacks. Another 53% say that their organization and their suppliers share the responsibility. A lack of communication between organizations and third parties and insufficient due diligence could expose organizations to significant supply chain risk. Almost half of the organizations surveyed admitted that they don’t list security standards in their vendor contracts and 34% stated that they don’t regularly monitor and assess risk within their suppliers’ cybersecurity. With the rapid increase in supply chain attacks over the past few years, these findings are a bit troubling!
Microsoft’s Autopatch will simplify software updates: If you sometimes forget to update your Windows and Office software, we have good news! In July 2022, Microsoft will be releasing a new feature called Autopatch that will update your software automatically. Supported versions of Windows 10, 11 and 365 for Enterprise will benefit from this free feature. Microsoft stated that their goal is to close security gaps that result because of patches that aren’t applied quickly enough. As cybersecurity incidents continue to be a top source threat for many organizations and their vendors, every bit of extra support helps!
Top 3 legal issues related to the Ukraine invasion: Gartner has identified three categories that legal and compliance leaders should be focusing on during the ongoing invasion of Ukraine. The first issue is complex sanctions. Legal teams are advised to review contracts to identify impacted groups. Workforce issues are another top concern and it’s recommended that compliance leaders do things like identifying employee visa implications and reviewing planned statements to assess any areas that need guidance. The third issue of concern is cybersecurity, in which legal and compliance teams should partner with information security teams to review cyber insurance policies. These teams should also be involved in tabletop exercises and should communicate cybersecurity standards to their third-party vendors.
Healthcare breach notification failure is discovered in an audit: Connecticut-based Access Health CT was discovered to have 44 unreported data breaches during a recent audit. The breaches occurred between July of 2017 and March of 2021 - 34 of which were caused by a single call center vendor. The incidents were reported to the Attorney General, but they neglected to report to other agencies, which is required by state law. Most of the breaches were small, though one impacted over 1,000 clients. Reporting vendor data breaches may be a difficult task, but it’s worth considering the impact of failing to comply with regulatory requirements.
Guide to global supply chain due diligence laws: Regulators around the world are increasingly focusing on third-party suppliers, especially when it comes to due diligence. Legislation currently exists throughout North America, Brazil, Australia and parts of Europe, with specific attention to human rights and environmental issues. Finland, Romania, the Netherlands, Belgium and Hong Kong all have pending legislation. Brazil stands out as having one of the most visible settlements related to a case involving illegal immigrants and a failure to provide social rights. While organizations need to adhere to certain standards within their own operations, don’t forget about the need to extend those standards throughout the supply chain.
The key to ESG compliance in vendor management: Investors and consumers are no longer satisfied with the half-hearted attempts by organizations to address environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues. Regulators have heard their concerns and started responding with proposed mandates on reporting guidelines, which extends to organizations’ vendors. To stay compliant with ESG regulations, organizations must ensure that their vendor management programs include certain components. Vendor contracts should include the right to audit, both physically and through documentation. Organizations also need to consider ethical sourcing in their supply chains, even if it affects their bottom lines. Procurement protocols should be formalized and vendor management programs need to be more robust and extensively governed.
Recently Added Articles as of April 7
The new month begins with an American Express outage, a cyberattack on an Indian bank and a look at operational resilience from financial regulators. Learn how to assess your vendors’ exposure on the dark web and why it’s better to simplify vulnerabilities in healthcare. Supplier performance management is also important to review and read up on the highlights of Utah’s privacy law. Check out the articles below for the top headlines this week.
Protecting against third-party cyber risk: You’ve probably heard the saying, “a chain is only as strong as the weakest link” and the same concept applies to cyber risk. Most companies need to outsource at least some of their business activities and this reliance on third parties leads to an increased exposure to cybersecurity incidents. Fortunately, there are strategies you can take to mitigate these risks. First, it’s important to assess your vendors’ cyber risk and mitigate any vulnerabilities you find. Ask your vendors to provide information on their security protocols and compare their processes with your own. Many organizations turn to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework as a guideline for their vendor risk assessments and it’s always important to maintain regular cyber check-ins to ensure your vendors are staying safe.
Indian bank learns a hard lesson after a cybersecurity attack: The Andra Pradesh Mahesh Co-Operative Urban Bank must have thought it was immune to cybercriminals, but quickly learned that's not the case when they successfully made off with millions of rupees. Local police revealed that a phishing attack resulted in a Remote Access Trojan and the bank neglected to use any sort of intrusion protection system. A poor password policy allowed the bank’s super users to use identical passwords and the attackers were able to create new bank accounts to transfer funds. The police report further stated that the bank didn’t have a proper network infrastructure and lacked several basic security tools. It’s still unknown what kind of repercussions the bank will receive, but it’s probably safe to say that they’ll begin focusing more on their security standards.
The role of CIOs in ESG strategies: As climate risk disclosures are gaining more attention from regulators, chief information officers (CIOs) need to understand the challenges that come from being an “ethical guardian” within their organizations. If passed, the SEC’s proposed rule on climate risk will require disclosures on various issues such as greenhouse gas emissions. Electricity, vehicles and corporate travel all have carbon impacts which CIOs will need to address. Social issues, both within an organization and its supply chain, is another important area of focus that CIOs should recognize. Wage rates, safety records and vulnerable migrant workers are all components of the “S” in environmental, social and governance (ESG). Experts warn that Excel spreadsheets will no longer be sufficient if the SEC rule is approved. Organizations will need to adopt sophisticated systems to ensure that they and their supply chain comply with regulations.
Your vendors’ exposure on the dark web: Do you know your dark web score? What about the scores of your vendors? Exposure to the dark web is a serious threat that organizations need to manage and that risk is even greater when you consider all the vendors that have access to your data. Some experts argue that traditional internal assessments and penetration testing don’t necessarily evaluate cyber risk over time. Dark web exposure ratings have the advantage of providing monitored updates while continuously searching for what’s on the dark web already. Measurable and comparable dark web scores can give business leaders better insight into their vendors’ cyber risk and, by extension, their organization’s own risk environment.
How to simplify vulnerabilities in healthcare: Third-party cyberattacks are a very real threat to the healthcare industry, but some experts believe that a “fear-based narrative” may do more harm than good. Healthcare providers are often warned about hypothetical dangers that exist within vulnerable devices such as an attacker potentially compromising an infusion pump. In reality, cybercriminals are more likely to carry out an attack that’s scalable rather than one that just affects a few devices. Healthcare providers are urged to prioritize addressing vulnerabilities found in their legacy infrastructure, server appliances and VPN.
American Express users face widespread outage: Amex customers recently experienced log in issues and difficulties making online payments after an hours-long outage halted operations. Many were also unable to contact customer service reps which caused further confusion. Users were asked for a one-time verification code multiple times and couldn’t gain access to their dashboards, though a source close to the incident confirms that a cyberattack was not the cause. This event should serve as an important reminder for organizations to assess their business continuity plans. An outage that lasts several hours is likely to cause a significant impact to not only business operations, but customer satisfaction, too.
Regulators turn their focus on operational resilience: The Federal Reserve, the OCC and the PRA are three of the top financial regulators that are emphasizing the importance of business resilience. The past few years have brought on increasingly volatile conditions, with no signs of slowing down, and financial institutions need to prepare for the times ahead. A core component of the UK’s supervisory statement SS1/21 is the implementation of strong and flexible third-party risk management capabilities which is a requirement that’s also outlined in U.S. interagency guidance.
Cyberattackers are diversifying their healthcare targets: According to recent breach reports, healthcare entities that provide benefits plans, staffing and rural medical services are just some of the latest victims of cyberattacks. The Conti ransomware group successfully carried out an attack that impacted the nonprofit firm Law Enforcement Health Benefits, Inc. (LEHB). The nonprofit ultimately paid a $100,000 ransom to obtain a decryptor so they could gain access to their systems. The incident is still being investigated, but LEHB has since confirmed that they’ve changed its email services vendor and implemented additional security measures. Experts say that healthcare organizations are usually under-invested when it comes to security making them an easier target than other sectors like finance. And, with third parties expanding an organization’s risk environment, it’s even more critical to implement stronger security practices.
Ukraine’s impact on third-party risk management: The ongoing war between Ukraine and Russia has highlighted the impact of sanctions as well as various third-party risks including cyber and operational. Incident management and business continuity plans are under more scrutiny as organizations try to meet expectations surrounding operational resilience. Some of the immediate effects organizations are seeing is the unavailability of Ukraine-based employees from third parties and product or service disruptions. Vendors are also seeing an increase in due diligence requests which can lead to inconsistent and delayed responses.
Spring Framework releases emergency patch: A critical zero-day bug known as CVE-2022-22965 has prompted Spring Framework to release an emergency patch. If exploited, the flaw may allow an attacker to obtain control of the targeted system. Users of Spring Framework are urged to upgrade to versions 5.3.18 or later and 5.2.20 or later. Spring.io gave credit to cybersecurity firm Praetorian for notifying them of the flaw.
Highlights of Utah’s privacy law: The Utah Consumer Privacy Act (UCPA) will officially go into effect December 31, 2023, but it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with some of the highlights to ensure compliance. The law differs from California’s act in that it has no private right of action. It also exempts entities covered by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, but only protected health information subject to HIPAA. Organizations are required to use “reasonable” data security practices, though these will depend on the size, scope and type of business. Overall, the UCPA is narrower than existing laws, so organizations shouldn’t expect any additional burdens.
An overview of IT outsourcing regulations: The financial services industry has seen rapid digital transformation over recent years, so it may be wise to brush up on some current regulatory guidelines. To begin, it’s important to know the governing bodies that oversee third-party risk management (TPRM) in financial institutions. The Prudential Regulatory Authority (PRA) oversees financial outsourcing in the UK and Ireland while the Digital Operational Resilience Act and European Banking Authority play this role in the EU. Over in the U.S., TPRM guidelines are handed out by the FDIC, the OCC and the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Regulatory scrutiny on third parties is rising and financial institutions are expected to implement pre-developed measures to maintain resilience while also accounting for data recovery. In addition, business continuity plans, exit strategies and third-party risk assessments are all important components to include in a TPRM program.
Four steps to succeed in supplier performance management: If you're struggling to maintain an efficient supplier performance management (SPM) program, this article is for you! A sustainable SPM program should begin by eliminating tedious spreadsheets and irrelevant surveys. Instead, consider using SPM software to obtain relevant supplier data. The second step is to take a science-based approach when asking your suppliers questions. Ask questions that are open-ended and context-gathering. This allows for a better understanding of a supplier’s ongoing performance. Step three is to measure both qualitative and quantitative data so you can have a holistic view of your suppliers. The final step is to solicit feedback from your suppliers so they can better align with your interests.
MFA bombing technique gives hackers an advantage: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an essential security practice, but some forms are weaker than others. Some hackers are able to bypass these weaker forms of MFA, such as one-time passwords sent by text or push prompts. Hacking group Cozy Bear has been found to bypass push prompts by issuing multiple MFA requests to the user’s legitimate device until the authentication is accepted. Hackers are essentially annoying the user into acceptance and experts are pointing out that this technique isn't new. MFA is still a critical practice, but one that shouldn’t be used alone. It’s more important than ever to stay informed of any emerging tactics that hacking groups are utilizing so your organization can stay protected from cyber threats both internally and from your vendors.
Related Posts
Low and High-Value Vendors
While third-party risk management (TPRM) doesn't usually generate revenue, it does enhance the...
Managing IT Vendor Security Risk
Through your vendor risk management program, you’re supposed to monitor your vendor’s information...
Vendor Consolidation Doesn’t Limit Risk in Third-Party Risk Management
Consumer data fulfillment services come in all shapes and sizes and include credit reporting firms,...
Subscribe to Venminder
Get expert insights straight to your inbox.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a personalized solution demonstration to see if Venminder is a fit for you.